DIFFERENT TYPES OF ARM MOVEMENT
-
Flexion: Bend the arm at the elbow or raise the arm forward:
Kneeling Bicep Curl
Back Platform Front Raise
Extension: Straighten arm at the elbow or move it backward
Kneeling Tricep Extension
Rear Delt Fly
-
Abduction: Lift arms away from the body:
Lateral Raise
Batwing
Adduction: Bring arm back toward the midline of the body
Tailbone Chest Fly
Heavy Chest Fly
-
Internal Rotation: Rotate arm inward towards the body
Chest Fly
External Rotation: Rotate arm outward
Newspaper
High Row
-
A circular motion of the arm. Combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Arm Circles
-
Horizontal Abduction: Move arm away from the midline while at shoulder height
Kneeling Rear Delt Fly
Heavy Rear Delt Fly
Floor Rear Delt Fly
Tailbone Rear Delt Fly
Horizontal Adduction: move arm toward the midline at shoulder height
Tailbone Chest Fly
Chest Fly w/ a Glute Bridge
-
Push: Move away from the body
Push-Ups
Heavy Chest Press
Heavy Tricep Press
Pull: Move toward the body
Kneeling Lat Pull
Bicep Curls
Rows
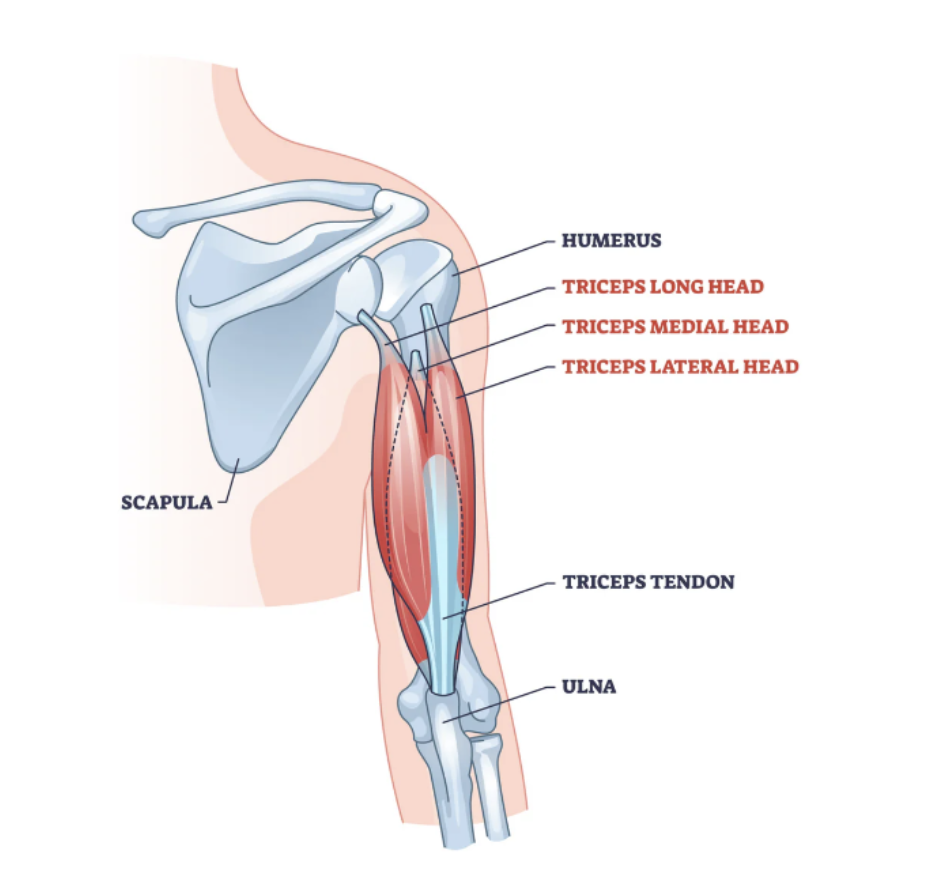
TRICEPS
The Triceps have three heads; Long, Medial, and Lateral, that connect the humerus (upper arm) and scapula (shoulder blade)
It’s function is to extend the elbow and bring the arm down to the body (adduction) - mostly done by the long head
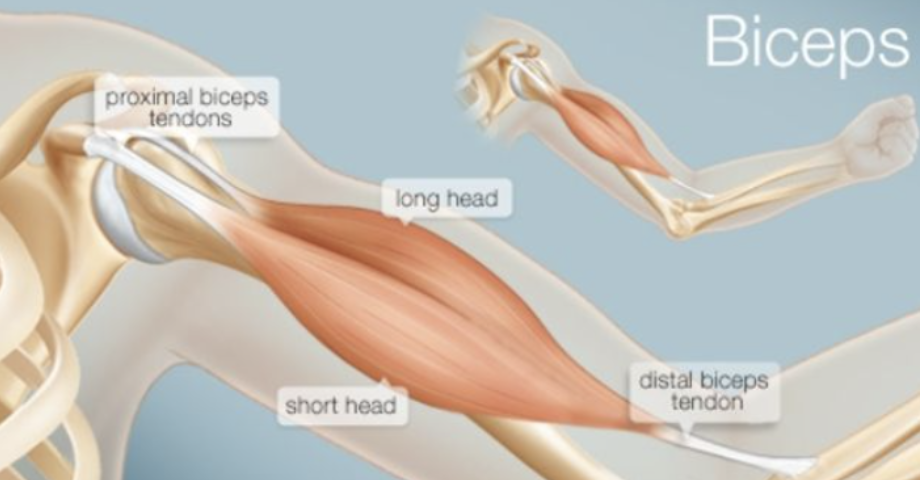
BICEPS
The biceps anatomy consists of the long head and short head muscles
Function:
Move the forearm towards the shoulder (elbow flexion)
Turning the hand from palm down to palm up
Help pull and curl vs most upper body muscles that push and press
Biceps make up about 40% of the arms so it is quicker to fatigue than the Triceps
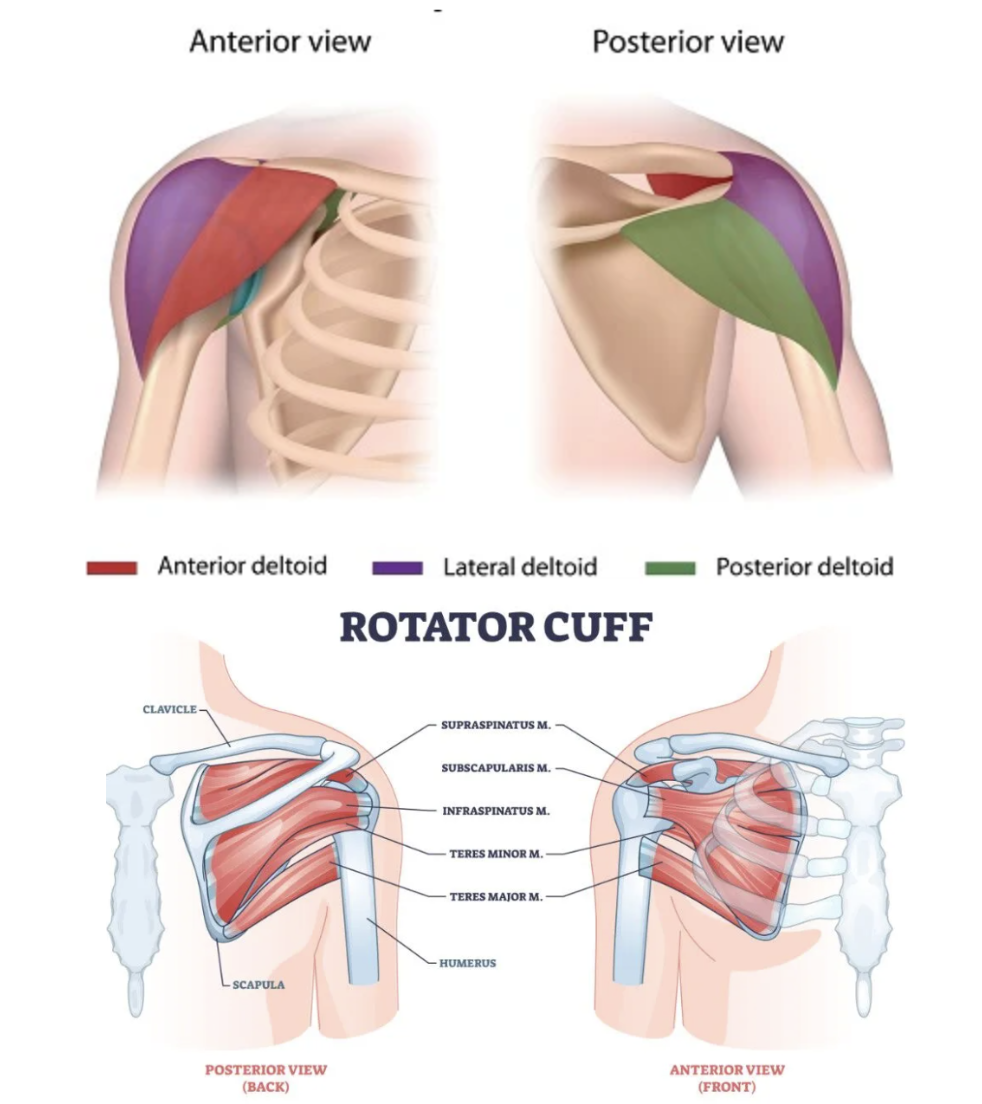
SHOULDERS
Muscles in the Shoulder:
Anterior Deltoid: Front of the shoulder. They move the arms overhead + in front you (front raises + pressing exercises)
Lateral Deltoid: Located on the outside of your shoulder, and helps you raise your arm out to the side
Posterior Deltoid: Located on the back of the shoulder it’s main function is to pull your arms backwards to bring your shoulder blades together (chest opener + newspaper)
Rotator Cuff Muscles: There are 4 muscles within the rotator cuff. IT is complex and delicate. Their job is to stabilize the shoulder and allow the upper arm to rotate or have range of motion.
Infraspinatus
Subscapularis
Supraspinatus
Teres Minor
Function
Deltoids: Move the arm away from the body (abduction)
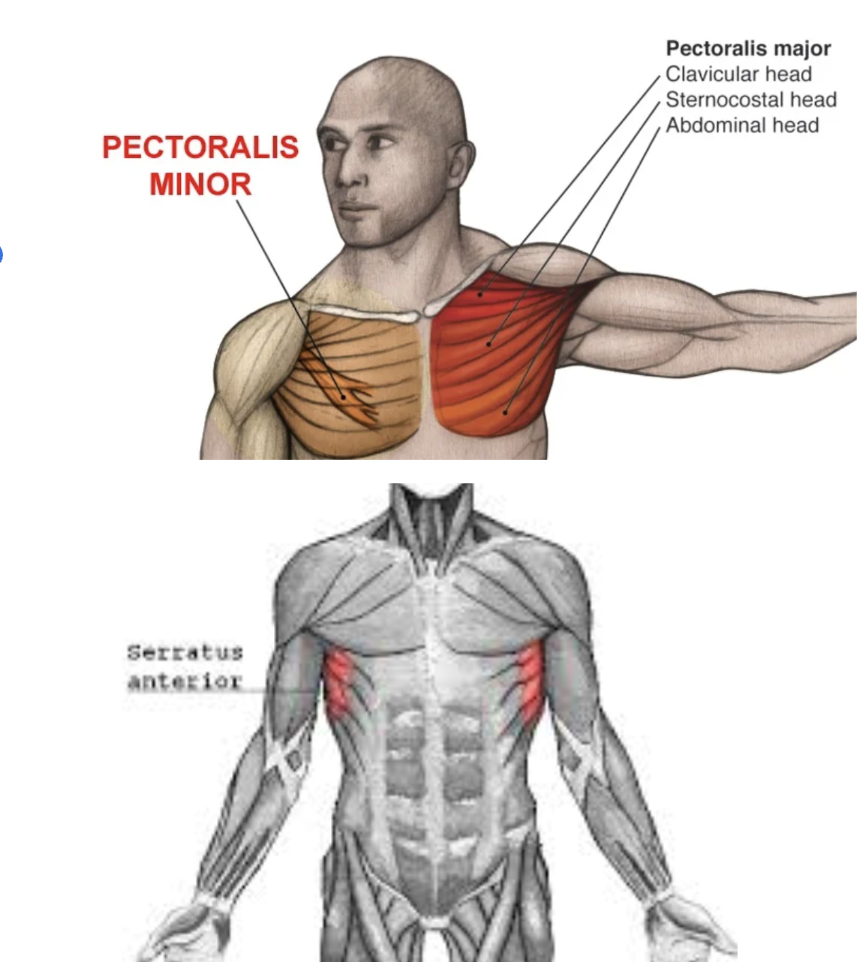
CHEST
The chest is part of a large group of “pushing muscles” in the upper body. (chest press, push-ups, lifting)
The three chest muscles
Pectoralis Major: This large, fan-shaped muscle starts at the clavicle, ribs and sternum, and inserts into the humerus (upper arm bone from elbow to shoulder) It’s function is to bring the humerus across the chest and help flex the shoulder to move your arm toward and across your chest (chest flies)
Pectoralis Minor: This thin triangular muscle is underneath the pec major and attaches to ribs 3-5 to reach the scapula (shoulder blade). It’s job is to help pull the shoulder forward and down.
Serratus Anterior: This honorary chest muscle attaches to the pecs on the ribs. It’s job is to move the scapular forward and upward (used heavily in plank based moves especially WB, Cobra, and Saw)
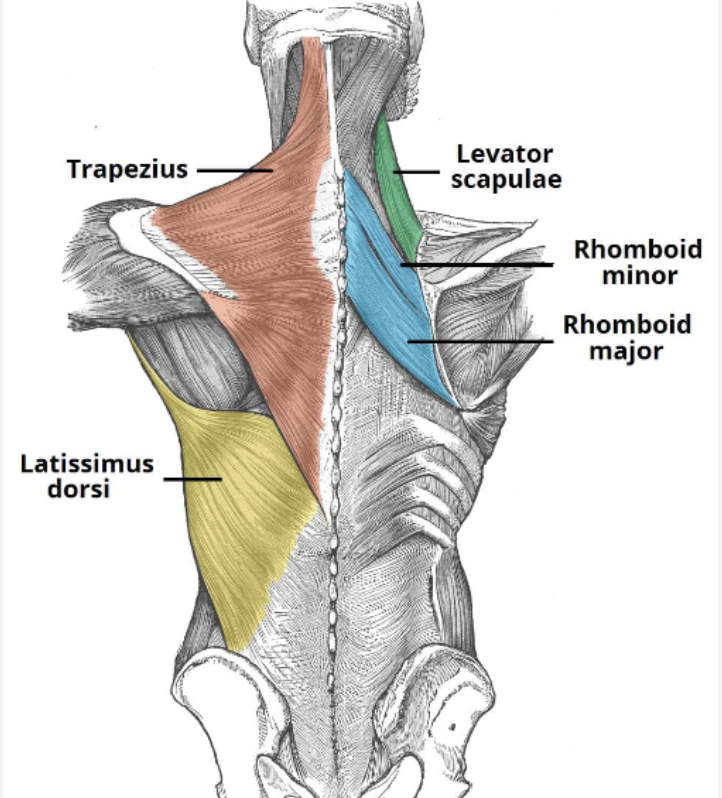
BACK
The back has some of the biggest muscles both in size and function in the upper body. They help us stand up straight, protect the spine, reach, pull, and extend our arms + torso.
5 Major Muscles
Latissimus Dorsi: Largest muscle in back and can provide force in various ranges of motion. Attached to upper end of the humerus and run down the vertebral column. They help you pull, reach as well as act as stabilizers in plank based movements
Trapezius: The traps help you shrug, pull the shoulder blades back, and down. It runs down the upper section of the spinal cord at the base of the skull attaching to the middle of the back.
Erector Spinae: (check in core)
Rhomboid: This upper back muscle lives under the traps. It helps us squeeze the scapula (bent over rows)
Teres Major: This small muscle lives under the lats and helps both the lats and rotator cuff muscles. It helps pull the arms down and rotate them inward.